- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Hydraulic Cylinders
- Forklift Hydraulic Cylinders
- Agricultural Machinery Hydraulic Cylinders
- Aerial Work Vehicle Hydraulic Cylinders
- Sanitation Machinery Hydraulic Cylinders
- Construction Machinery Hydraulic Cylinders
- Mobile Machinery Hydraulic Cylinders
- Industrial Engineering Hydraulic Cylinders
- American Standard Series Hydraulic Cylinders
- Offshore Hydraulic Cylinders
- Energy Technology Hydraulic Cylinders
- Tunnel Boring Machine Hydraulic Cylinders
- Telescopic Hydraulic Cylinders
- Tractor & Front End Loader Hydraulic Cylinders
- Steering Hydraulic Cylinders
- Dump Truck & Trailer Hydraulic Cylinders
- Electirc and Instrument
- Gasification station
- Equipment
- Gas compressor
- Gas filter and purification
- Gas Storage & transportation
- Air separation plant
- Refrigeration Equipment
- Ungrouped
- Hydraulic Cylinders
- News
- Download
- Send Inquiry
- Contact Us

Drive Shaft
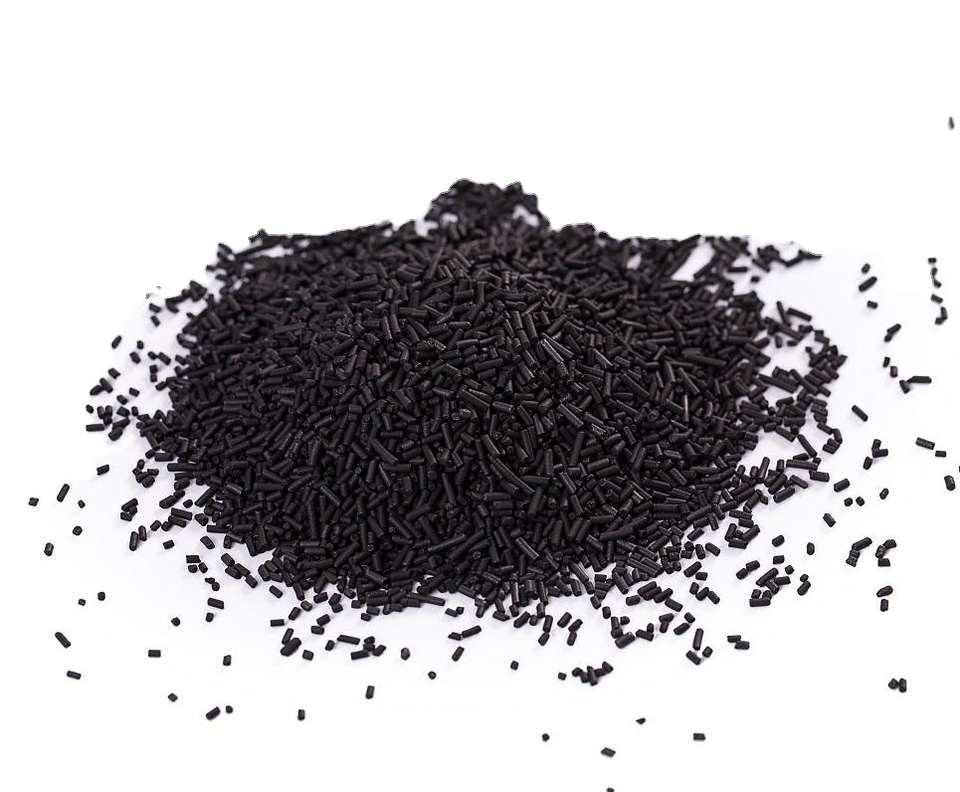
We warmly welcome friends from all over to visit and establish long-term, mutually beneficial cooperation!How Are Activated Carbon Adsorbents Used?
How Are Activated Carbon Adsorbents Used? Imagine your factory is facing a tough environmental compliance inspection or your product quality is suffering due to volatile organic compound (VOC) contamination in the air or water. This is a common yet critical pain point for industrial procurement managers. Activated carbon adsorbents are the silent, powerful workhorses solving these exact problems. They are porous materials with a massive surface area that acts like a magnet, trapping and holding unwanted chemicals, odors, and impurities from gases and liquids. From purifying drinking water and controlling industrial emissions to recovering precious solvents in manufacturing, their applications are vast. Understanding their use is key to operational efficiency and regulatory success. For a reliable partner in this essential technology, consider Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited, a leader in providing high-performance adsorption solutions that directly tackle these industrial challenges.
Article Outline:
- Tackling Air Pollution and Emission Control
- Ensuring Water Purification and Safety
- Mastering Solvent Recovery and Manufacturing
- Choosing the Right Activated Carbon
- FAQs on Activated Carbon Usage
Tackling Air Pollution and Emission Control Head-On
Your plant emits fumes containing hazardous VOCs or unpleasant odors, risking non-compliance with stringent EPA regulations and creating community relations issues. The solution lies in strategically implemented activated carbon adsorption systems. These systems force contaminated air through beds of activated carbon, where pollutants are captured within the carbon's microscopic pores, allowing clean air to exit. This is critical for industries like chemical manufacturing, painting, and pharmaceuticals. Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited offers tailored systems designed for high adsorption capacity and long service life, ensuring you meet emission standards reliably.
| Application Scenario | Target Pollutants | Key Carbon Parameter (from Raydafon) |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Exhaust Fumes | VOCs, Solvents, Odors | High Iodine Number (1000+ mg/g) |
| Indoor Air Purification | Formaldehyde, Smoke | Specially Impregnated Formulations |
| Landfill Gas Treatment | Hydrogen Sulfide, Mercaptans | High Surface Area (1000-1500 m²/g) |
Ensuring Water Purification and Process Safety
Contaminants in process water or wastewater can shut down production lines and lead to costly fines. Whether it's discoloration, organic chemicals, or chlorine taste in final product water, activated carbon filtration provides a robust solution. Water is passed through granular or block carbon filters, where contaminants are adsorbed, resulting in purified water. This is essential for food & beverage production, municipal water treatment, and electronics manufacturing. Raydafon's activated carbons are engineered for optimal pore structure to remove specific contaminants efficiently, safeguarding your water quality and process integrity.
| Application Scenario | Target Contaminants | Key Carbon Parameter (from Raydafon) |
|---|---|---|
| Drinking Water Treatment | Chlorine, TOCs, Pesticides | High Methylene Blue Value |
| Wastewater Polishing | Dyes, Phenols, Heavy Metals* | Steam-Activated, High Hardness |
| Ultrapure Water for Electronics | Trace Organics, Ions | Acid-Washed, Low Ash Content |
Mastering Solvent Recovery and Manufacturing
In processes like printing, coating, or chemical synthesis, expensive solvents evaporate into exhaust streams, representing significant financial loss and environmental burden. Activated carbon adsorption enables solvent recovery. Solvent-laden air is adsorbed onto the carbon. Subsequently, the carbon bed is regenerated using steam or hot air, desorbing the concentrated solvent, which is then condensed and reused. This cuts raw material costs and reduces waste. Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited provides high-quality, durable activated carbons with excellent adsorption and desorption characteristics, maximizing your recovery rates and ROI.
| Application Scenario | Common Solvents Recovered | Key Carbon Parameter (from Raydafon) |
|---|---|---|
| Printing & Coating Operations | Acetone, Toluene, IPA | High Butane Working Capacity |
| Pharmaceutical Synthesis | Methylene Chloride, Ethanol | Uniform Particle Size, High Purity |
| Adhesive Manufacturing | Hexane, Heptane | Optimized Pore Size Distribution |
Choosing the Right Activated Carbon for Your Needs
Selecting the wrong type of carbon leads to premature exhaustion, inefficient operation, and higher costs. The key is matching carbon properties to your specific contaminant and process conditions. Factors like raw material (coconut shell, coal, wood), activation method, pore size distribution, and surface chemistry are critical. Raydafon's technical team excels at this precise matching, offering a wide portfolio and expert consultation to ensure you get the most cost-effective and efficient Adsorbent for your unique application, solving your problem at its core.
| Selection Factor | Consideration | Raydafon's Solution Range |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Defines hardness, pore structure, and ash content. | Coconut Shell, Coal-Based, Wood-Based Carbons |
| Pore Size | Micropores (small molecules), Mesopores (larger organics). | Tailored Pore Structures for Target Molecules |
| Impregnation | Adds chemicals for specific gases (e.g., H2S, Mercury). | Custom Impregnation Services Available |
FAQs on How Activated Carbon Adsorbents Are Used
Q: How long does activated carbon last before it needs replacement?
A: The service life depends entirely on the concentration of contaminants, airflow or water flow rate, and the type of carbon used. It can range from a few months in heavy industrial use to over a year in lighter applications. Monitoring pressure drop or effluent quality is key. Raydafon provides performance estimates and support for optimal change-out scheduling.
Q: Can used activated carbon be regenerated and reused?
A: Yes, many types of activated carbon, especially those used for solvent recovery or gas purification, can be thermally regenerated off-site to restore most of their adsorption capacity. This is more economical and sustainable than single-use disposal for certain high-volume applications. Raydafon offers guidance on carbon regeneration feasibility for your specific process.
We hope this guide clarifies the powerful applications of activated carbon adsorbents. Have a specific challenge involving air, water, or solvent purification? We invite you to share your scenario or questions in the comments below.
For expert solutions in adsorption technology, partner with Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited. As a dedicated manufacturer and supplier, we specialize in providing high-performance activated carbon products and systems tailored to meet industrial purification and recovery needs. Visit our website at https://www.raydafon-hydraulic.com to explore our capabilities, or contact our sales team directly at [email protected] for a customized consultation.
Smith, J.A., 2022, Mechanisms of Organic Compound Adsorption onto Activated Carbon, Environmental Science & Technology, 56(3).
Chen, L., & Wang, F., 2021, Advanced Pore Structure Design of Activated Carbons for VOC Removal, Carbon, 185.
Johnson, R.L., et al., 2020, Comparative Study of Biomass-Based Activated Carbons in Water Treatment, Journal of Hazardous Materials, 400.
Kim, S., & Park, H., 2019, Regeneration Strategies for Spent Activated Carbon: A Review, Chemical Engineering Journal, 375.
Davis, M.E., 2018, Adsorption Processes for Air Pollution Control in Industrial Settings, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 57(45).
Li, Y., Zhang, G., 2017, The Role of Surface Chemistry in Activated Carbon Adsorption, Langmuir, 33(50).
Garcia, T., et al., 2016, Solvent Recovery Using Activated Carbon Adsorption: Process Optimization, Separation and Purification Technology, 171.
Ozekin, K., & Karanfil, T., 2015, The Impact of Activated Carbon Characteristics on Disinfection Byproduct Removal, Water Research, 85.
Patel, H., 2014, Activated Carbon from Alternative Raw Materials: Properties and Applications, Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 110.
Muller, E.A., & Gubbins, K.E., 2013, Molecular Simulation Study of Adsorption in Activated Carbon Pores, Adsorption, 19(1-2).
Related News
- Are Oil-Free Air Compressors Better Than Oil-Lubricated Ones?
- What is the role of silence in music and artistic composition?
- What is an air filter and how does it work?
- What are the main components of an absorption chiller?
- How to replace a steering hydraulic cylinder?
- What are the key specifications to consider when ordering telescopic cylinders?
Leave me a message
New Products